Inflammaging: Effective Strategies to Combat Age-Related Inflammation
Inflammaging is the chronic, low-grade inflammation that increases as we age, driving aging and age-related diseases. Understanding inflammaging and its impact is crucial for promoting healthy aging. In this article, we will explore its mechanisms, influences, and strategies to combat it effectively.
Key Takeaways
Inflammaging describes chronic, low-grade inflammation that increases with age, driven by factors such as cellular senescence and dysregulated immune responses.
Lifestyle interventions, including diet, exercise, and stress management, play a crucial role in mitigating the effects of inflammaging and promoting healthy aging.
Emerging therapies, such as senolytic drugs and Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT), show promise in reducing chronic inflammation and addressing the underlying mechanisms of age-related diseases.
Understanding Inflammaging
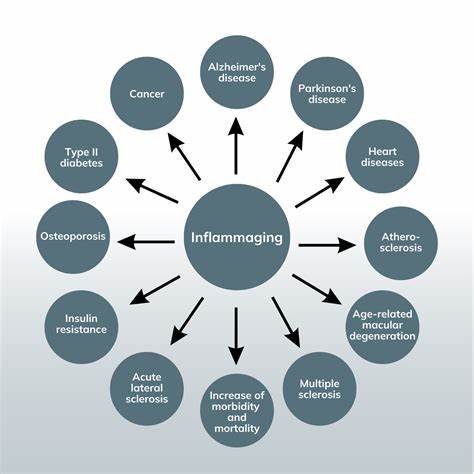
Inflammaging is a term that perfectly describes the chronic, low-grade inflammation that becomes more prevalent as we age. Unlike the acute inflammation that occurs in response to injuries or infections, chronic inflammation persists over time, often without obvious symptoms. As we age, our bodies experience an increase in pro-inflammatory factors that surpass anti-inflammatory factors, leading to a state of constant, low-grade inflammation.
This systemic inflammation is not just a byproduct of aging but a driving force behind it. The inflammatory response, which is meant to protect and heal, becomes dysregulated. The balance tips in favor of chronic inflammation, setting the stage for a host of age-related changes and diseases. Inflammaging is not just about feeling older; it’s about the cellular and molecular chaos that accelerates the aging process itself.
To fully grasp inflammaging, we must delve into its underlying mechanisms and the genetic and environmental influences that shape it. Understanding these factors helps in creating strategies to promote healthy aging and reduce chronic low-grade inflammation.
The Mechanisms Behind Inflammaging
At the heart of inflammaging lies cellular senescence, a state where cells lose their ability to divide and function normally. These aging cells secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6 and TNF, which contribute to chronic inflammation. The accumulation of these senescent cells and their inflammatory output is a hallmark of inflammaging, disrupting tissue function and promoting age-related diseases.
Immunosenescence, the aging of the immune system, exacerbates this problem. As we age, both our innate and adaptive immune responses decline, leading to a reduced ability to fight infections and a heightened state of chronic inflammation. The immune system’s shift from a protective role to a pro-inflammatory state is a key driver of inflammaging.
This dysregulated immune response is further compounded by the exhaustion of immune cells. Over time, immune cells become less effective at responding to inflammatory stimuli, leading to a persistent inflammatory state. Understanding these mechanisms sheds light on why chronic low-grade inflammation becomes a persistent feature of human aging and a major contributor to age-related chronic diseases.
Genetic and Environmental Influences
Genetics and environment are the twin pillars that shape the landscape of inflammaging. Genetic predispositions can influence the levels of inflammatory markers in our blood, affecting our susceptibility to age-related diseases. These genetic factors interact with environmental influences, such as diet, physical activity, and exposure to pollutants, to modulate the balance between inflammation and anti-inflammation.
Personalized medicine, which tailors treatment based on individual genetic profiles and environmental factors, holds promise for combating inflammaging effectively. By understanding an individual’s unique inflammatory profile, we can develop targeted interventions that address the specific drivers of their chronic inflammation. This approach could revolutionize the way we manage age-associated inflammation and promote healthy aging.
Regular physical activity and stress management are also crucial in reducing inflammation. Practices like mindfulness and meditation can lower stress-related inflammation, highlighting the importance of lifestyle modifications in managing inflammaging. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) is another innovative approach that helps reduce inflammation and promote healing from the inside out.
The Role of the Immune System in Inflammaging
Chronic inflammation is a double-edged sword, fueling the onset and progression of various chronic diseases that can accelerate aging.
The immune system, which is supposed to protect us, becomes a major player in this process. As we age, the immune system’s ability to regulate inflammation diminishes, leading to a state of systemic inflammation.
This chronic inflammatory state is linked to:
frailty
cardiovascular diseases
sarcopenia
anemia
osteoporosis
mitochondrial dysfunction
The inflammatory response becomes dysregulated, with increased serum levels of inflammatory cytokines like IL-6 and TNF- acting as strong risk factors for multimorbidity in elderly individuals. These cytokines fuel a cycle of inflammation that perpetuates age-associated diseases. Recognizing the immune system’s role in inflammaging helps in crafting strategies to reduce its impact and enhance healthy aging.
Immunosenescence and Chronic Inflammation
Immunosenescence, the gradual decline of the immune system with age, is a key driver of chronic inflammation. This decline results in diminished immune responses, perpetuating the cycle of low-grade inflammation associated with aging. Genetic variations can also influence the levels of inflammatory markers in the blood, affecting an individual’s risk for age-related diseases.
The senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) plays a significant role in this process. Senescent cells secrete inflammatory cytokines, growth factors, and proteases, contributing to the persistent inflammatory state. These inflammatory factors disrupt tissue function and promote the development of age-related chronic diseases such as chronic kidney disease and cognitive decline.
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) has emerged as a promising intervention to combat immunosenescence by helping eliminate the genes associated with inflammation and cell death. Addressing the mechanisms of immunosenescence allows for the development of better strategies to decrease chronic inflammation and support healthy aging.
Impact of Viral Infections
Chronic viral infections (like long covid) can maintain immune activation and alter the levels of inflammatory markers, exacerbating the effects of inflammaging. Persistent infections like cytomegalovirus (CMV) lead to immune system alterations that can increase disease risk and inflammation. These infections cause a reduction in T cells diversity, contributing to a weaker immune response in the elderly.
The continuous presence of viral infections keeps the immune system in a state of heightened alert, perpetuating chronic inflammation. This persistent immune activation can lead to adverse health outcomes, including increased susceptibility to age-related diseases.
Recognizing the impact of viral infections on inflammaging aids in creating interventions to lessen their effects and boost immune system function in the elderly.
Health Implications of Inflammaging
The health implications of inflammaging are far-reaching, affecting virtually every system in the body. Elevated levels of inflammatory markers in older adults lead to greater susceptibility to chronic diseases and disability. Chronic inflammation is often linked to increased risks of cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, cognitive decline, and various age-associated conditions.
The aging immune system contributes significantly to this process, as it leads to a state of chronic inflammation that is a major factor in various age-related diseases. Grasping the health implications of inflammaging is key to devising strategies to reduce its impact and enhance health outcomes in older adults.
Cardiovascular Disease
Chronic inflammation is both a risk factor and a mechanism contributing to cardiovascular disease. People with high inflammation levels have a 2-3 times higher risk of developing heart disease compared to those with low inflammation levels. Inflammation causes an energetic imbalance towards catabolism, leading to frailty in older adults with cardiovascular disease.
Modulating inflammation can prevent cardiovascular diseases in older individuals. However, not all anti-inflammatory treatments are effective; for instance, high doses of infliximab did not improve moderate-to-severe congestive heart failure and even worsened the condition.
Recognizing inflammation’s role in cardiovascular disease is vital for creating effective interventions.
Type 2 Diabetes
Inflammation is a key factor in the development of insulin resistance, which is a precursor to type 2 diabetes. Chronic inflammation is linked to insulin resistance, playing a significant role in the development of type 2 diabetes. Elevated levels of inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-1β and IL-6, are associated with an increased risk of type 2 diabetes.
Managing chronic inflammation is key to preventing and treating type 2 diabetes. Understanding the link between inflammaging and diabetes can help develop targeted interventions that address the inflammatory processes driving insulin resistance.
Cognitive Decline and Neurodegenerative Diseases
Chronic inflammation is linked to neurodegenerative diseases, with pro-inflammatory cytokines playing a role in cognitive deterioration. Inflammation is a critical factor contributing to cognitive decline and diseases like Alzheimer’s. Chronic low-grade inflammation is thought to influence the pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative conditions.
Elevated inflammatory markers in the brain have been implicated in the progression of cognitive impairment in older adults. Recognizing inflammation’s role in cognitive decline is important for developing strategies to maintain cognitive health and mitigate neurodegenerative diseases.
Lifestyle Interventions to Mitigate Inflammaging
Lifestyle interventions play a crucial role in combating chronic inflammation associated with aging. Adopting a healthy diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress effectively can significantly lower chronic inflammation and promote healthier aging.
Incorporating these lifestyle changes helps reduce the effects of inflammaging and enhance overall well-being, promoting healthy ageing.
Diet and Nutrition
Environmental factors, including diet and lifestyle, play a critical role in modulating the balance of inflammation in the body. Following the Mediterranean diet, which is rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and fish, can help reduce inflammatory markers linked to aging. Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants, like fatty fish and leafy greens, are particularly effective in combating inflammation.
Limiting sugar, refined carbs, and processed foods can also help reduce inflammatory responses in the body. A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods supports metabolic homeostasis and promotes healthy aging.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular exercise significantly reduces systemic inflammation and supports immune function, combating inflammaging. Engaging in consistent physical activity reduces the risk of developing inflammaging and is linked to a better likelihood of preventing or delaying its onset in older adults.
Moderate exercise is particularly effective in lowering inflammatory markers for sedentary older adults. Recommended physical activities to mitigate the effects of inflammaging include brisk walking, cycling, swimming, running, and resistance training.
It is never too late to adopt an active lifestyle, as staying physically active can lead to significant reductions in the effects of inflammaging.
Stress Management
Chronic stress can lead to increased inflammatory markers in the body, contributing to the process of inflammaging. Effective stress management techniques, including exercise and potentially the use of CBD, can improve overall well-being and reduce inflammation-related health risks. Engaging in consistent exercise can lower stress levels, which contributes to inflammation reduction.
CBD interacts with the endocannabinoid system to regulate the immune system and reduce inflammation, providing pain relief. Combining effective stress management practices with lifestyle changes can significantly reduce chronic inflammation and promote healthier aging.
Emerging Therapies for Inflammaging
Emerging therapies are shedding new light on how we can combat chronic inflammation associated with aging. Research indicates that understanding the molecular basis of inflammaging is crucial for developing targeted therapies.
From anti-inflammatory medications to senolytic drugs and Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT), these innovative treatments hold promise for reducing systemic inflammation and promoting healthier aging.
Anti-Inflammatory Medications
Clinical trials are focusing on various anti-inflammatory drugs to determine their effectiveness in addressing chronic inflammatory diseases. Anti-inflammatory medications, such as NSAIDs and corticosteroids, are being researched for their role in reducing chronic inflammation associated with aging. Results from these clinical trials suggest that anti-inflammatory drugs can have significant positive effects on managing chronic inflammation.
Ongoing research into anti-inflammatory medications holds promise for alleviating the effects of inflammaging. These medications can help modulate the inflammatory response and provide relief from the symptoms of chronic inflammatory diseases, ultimately contributing to healthier aging.
Senolytic Drugs
Senolytic drugs are specifically designed to target and eliminate senescent cells, which accumulate with age and contribute to chronic inflammation. By clearing these aging cells, senolytic drugs can lead to a reduction in systemic inflammation and alleviate symptoms associated with inflammaging. These drugs function by selectively inducing apoptosis in senescent cells, thereby reducing their detrimental effects on surrounding tissues.
Clinical trials are currently exploring the efficacy of senolytic drugs for aging-related diseases, with promising early results to support their potential in treating conditions exacerbated by inflammaging. By reducing the burden of senescent cells and associated inflammation, senolytic drugs could significantly improve healthspan and promote healthier aging.
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT)
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) is a treatment method involving inhalation of pure oxygen in a pressurized chamber, which enhances oxygen delivery to tissues and aids in healing. HBOT reduces inflammation by decreasing pro-inflammatory cytokines and stimulating the formation of new capillaries, thereby enhancing blood and oxygen delivery to deprived tissues. This therapy also activates vascular endothelial growth factors, which play a critical role in the healing process.
Patients paying for HBOT often report improvements in symptoms such as reduced pain, enhanced mobility, and overall well-being. HBOT promotes the mobilization of stem cells, significantly increasing their presence in the bloodstream following treatment. This method is known to stimulate angiogenesis, the process of new blood vessel formation, which aids in healing chronic wounds.
Additionally, HBOT has antimicrobial effects that enhance the immune response and help combat infections. Reducing chronic inflammation and enhancing natural healing processes makes HBOT a promising approach for managing inflammaging and improving health outcomes in older adults.
The Future of Inflammaging Research
The future of inflammaging research is bright, with recent innovations aiming to target the underlying mechanisms of inflammaging, including immunotherapy and novel anti-inflammatory agents. These innovative treatments focus on reducing chronic inflammation and addressing senescent cell accumulation, paving the way for more effective strategies to manage age-related inflammation.
An integrated Systems Medicine approach is needed to better understand the molecular core of inflammaging. By combining insights from various fields of research, we can develop a more comprehensive understanding of the inflammatory processes driving aging and devise more effective interventions to promote healthier aging.
Single-Cell Technology
Advancements in single-cell analysis technology are enabling the identification of specific immune cell types and their roles in inflammaging. Single-cell transcriptomics allows researchers to track changes in gene expression associated with aging and inflammation at a cellular level. These studies have revealed that aging increases transcriptional heterogeneity in cells, indicating greater variability in gene expression.
Single-cell RNA sequencing has shown specific inflammatory processes linked to distinct immune cell types in the context of aging. By investigating the distinct cellular behaviors and interactions contributing to the development of inflammaging, researchers can develop more targeted therapies to combat chronic inflammation and promote healthier aging.
Personalized Medicine
Personalized medicine is emerging as a potential strategy in combating age-related inflammation by considering individual genetic and environmental profiles. The importance of personalized treatment plans is emphasized, tailoring HBOT sessions to individual needs to ensure optimal results in managing inflammation. This approach can enhance the effectiveness of therapies aimed at reducing inflammation and promoting healthier aging.
An example of personalized treatment methods includes HBOT, which requires specific adjustments for each patient’s condition. By tailoring interventions based on individual inflammatory profiles and genetic backgrounds, personalized medicine has the potential to revolutionize the management of inflammaging and improve health outcomes for older adults.
Summary
Inflammaging, the chronic low-grade inflammation that accompanies aging, is a major driver behind many age-related diseases and conditions. Understanding the mechanisms behind inflammaging, including cellular senescence and immunosenescence, is crucial for developing effective strategies to combat it. Genetic and environmental factors also play significant roles in shaping the inflammatory landscape, highlighting the importance of personalized approaches to treatment.
The immune system’s role in inflammaging is both protective and detrimental, as chronic inflammation fuels the progression of various chronic diseases. Emerging therapies, including anti-inflammatory medications, senolytic drugs, and Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT), offer promising approaches to reducing systemic inflammation and promoting healthier aging.
Lifestyle interventions, such as adopting an anti-inflammatory diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress effectively, are also crucial in mitigating the effects of inflammaging. As research continues to advance, innovative technologies like single-cell analysis and personalized medicine hold the potential to revolutionize our understanding and management of age-related inflammation.
By incorporating these strategies and staying informed about the latest research, we can take proactive steps to combat inflammaging and promote a healthier, more vibrant aging process. The journey to healthier aging starts with understanding and addressing the root causes of chronic inflammation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the cause of inflammaging?
Inflammaging is primarily caused by an age-related increase in systemic chronic inflammation, influenced by factors such as oxidative stress, changes in the inflammatory cytokine network, and cellular senescence. These factors collectively contribute to the body’s deteriorating inflammatory response as it ages.
What is inflammaging?
Inflammaging is the persistent, low-grade inflammation that increases with age, leading to a higher risk of various age-related diseases. Understanding this concept is crucial for managing health in the aging process.
How does cellular senescence contribute to inflammaging?
Cellular senescence contributes to inflammaging by causing cells to lose their regenerative ability and secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines, leading to chronic inflammation and tissue dysfunction. This chronic inflammatory state exacerbates age-related diseases.
What role does the immune system play in inflammaging?
The immune system contributes to inflammaging through immunosenescence, which results in chronic inflammation that exacerbates age-related diseases. This decline highlights the critical interplay between aging and immune function.
How can lifestyle changes help mitigate inflammaging?
Making lifestyle changes such as improving your diet with anti-inflammatory foods, staying physically active, and managing stress can effectively reduce chronic inflammation and support healthier aging. These adjustments play a crucial role in mitigating inflammaging.